Tractor Safety: Essential Guidelines for Safe Operation
When it comes to operating a tractor, safety should always be the top priority. Whether you're a seasoned operator or a beginner, following these safety protocols can prevent accidents and ensure that you and others remain safe on the job.
 |
| Image Source: https://tractorguru.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/The-Steps-for-Safely-using-a-Farm-Tractor.jpg |
Key Safety Measures:
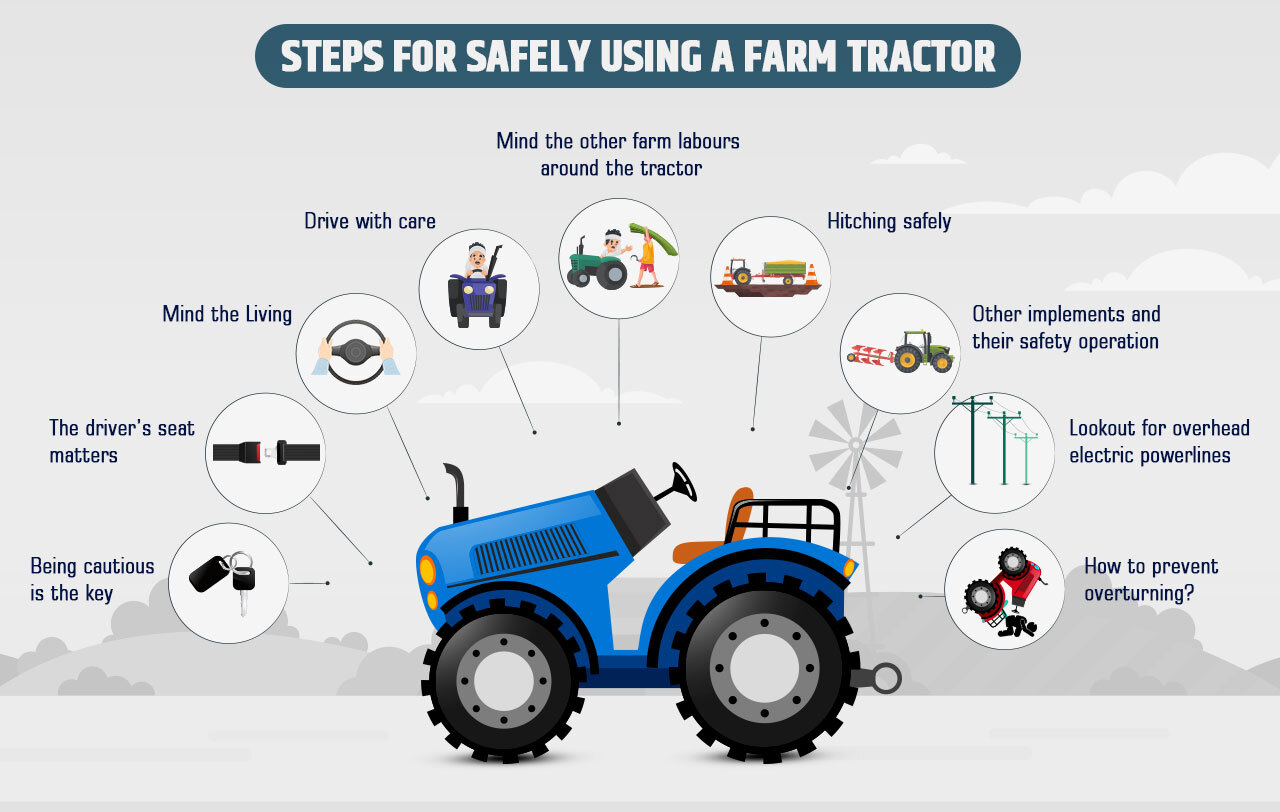
1.Slow-Moving Vehicle Emblems:
Ensure that all tractors are equipped with slow-moving vehicle (SMV) emblems. This makes your tractor more visible to others, especially on public roads.
2. Operator Safety Training:
Every tractor operator should receive comprehensive safety training. Understanding the risks and knowing how to mitigate them is crucial for safe operation.
3. No Seat, No Rider Policy:
Maintain a strict "no seat, no rider" policy. Tractors are not designed to carry passengers, and doing so can lead to serious injuries.
4. Securing the Tractor:
Before leaving the tractor, always remove the key, set the brakes, lock the transmission, and lower any attached implements.
Before Using a Tractor:
Familiarize yourself with the tractor and its safety features. Regularly review the operator's manual and adhere to the instructions on safety decals attached to the tractor.
Starting the Tractor:
Before starting, conduct a thorough check of the tractor, fasten your seatbelt, and adjust the mirrors. Ensure that the path is clear, then start the tractor and begin your work. If a vehicle needs to be jump-started, address the malfunction promptly to avoid unsafe conditions.
No Riders Policy:
Tractors are designed for one operator only. Never allow riders, especially children, as there is no safe place for anyone else on the tractor or its implements.
Training New Operators:
When training new or inexperienced operators, ensure they review the operator's manual and understand how to recognize and avoid hazards. Do not allow them to drive on public roads without a driver's license.
Keeping the Tractor Chemical-Free:
To keep the tractor cab free from harmful chemicals, remove personal protective equipment (PPE) before entering the cab. If the cab does not offer protection during product application, continue wearing PPE.
Suggestions to Maintain a Chemical-Free Cab:
- Remove contaminated soil and debris from shoes or boots before entering.
- Keep the floor clean by sweeping or vacuuming.
- Regularly wipe down the cab headliner and inside cowling.
- Clean the tractor exterior to reduce chemical exposure.
- Clean control knobs and the steering wheel with a grease-cutting agent.
- Avoid grasping the steering wheel with gloves worn during chemical mixing.
Refueling Safety:
Refueling tractors can be dangerous due to the risk of fire and explosion. Always refuel outside, and never while the engine is running or hot. Static electricity can ignite fuel, so ground the tractor to reduce this risk.
Carbon Monoxide Awareness:
Never start or work on a running engine in an enclosed space. Carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas, can be deadly.
Preventing Tractor Overturns:
Tractors can overturn easily. Equip them with rollover protective structures (ROPS). Avoid operating near ditches, embankments, and steep slopes. Reduce speed on rough or slick surfaces and carry heavy loads with extra caution.
Safe Hitching Practices:
Only hitch towed loads to the drawbar at the manufacturer's recommended height. Use proper clips and pins, and keep the hitch low to prevent the tractor from flipping over backward.
Appropriate Tractor Use:
Tractors are designed for specific tasks like carrying implements, transporting units, and providing remote power. Never use a tractor for joyriding, herding cattle, or other inappropriate tasks.
Finishing the Day Safely:
At the end of your workday, park the tractor in a safe place, disengage the PTO, lower implements, turn off the engine, and set the brakes. Always remove the key, and never leave the tractor in gear.
OSHA Safety Guidelines:
For those working under the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSHA), the following rules apply:
- Fasten the seatbelt if the tractor has ROPS.
- Avoid operating near dangerous areas like ditches or embankments.
- Reduce speed when turning or operating on rough surfaces.
- Use common hand signals to communicate with others in the area.
- Operate the tractor smoothly and avoid jerky movements.
- Hitch only to recommended drawbars and hitch points.
- Set the brakes securely and use park locks if available.
Ultimately, safety comes down to common sense and patience. While tractors are designed with safety in mind, the responsibility for safe operation rests with you, the operator. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a safer working environment for yourself and others.
Stay safe, and operate with caution!
Troubleshooting Common Tractor Engine Issues
Keeping your tractor's engine in optimal condition is essential for smooth operation and longevity. However, even the best-maintained tractors can experience issues. Here’s a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting some of the most common engine problems you might encounter, along with potential causes and solutions.
Engine Fails to Start
If your tractor engine is struggling to start, consider these potential issues:
- Fouled Spark Plugs or Faulty Breaker Points/Condenser: Check and replace if necessary.
- Loose Battery Terminals: Tighten the connections.
- Empty Fuel Tank: Refuel and check for leaks.
- Too Rich Fuel Mixture: Adjust the fuel mixture to the correct ratio.
- Faulty Diesel Pumps/Injection Nozzle: Inspect and repair or replace.
- Incorrect Valve Timing or Ignition: Check and reset timing.
- Seizure of Key Components (Crankshaft, Camshaft, Piston, Cylinder Liner, or Bearing): Requires professional inspection and repair.
- Air or Water in the Fuel System: Bleed the system and ensure proper fuel quality.
- Clogged Fuel Pipe or Filter: Clean or replace as needed.
- Low Cetane Number Fuel: Use a higher-quality fuel.
- Compression Leak in Cylinder Head: Inspect and repair leaks.
- Excessive Valve Clearance: Adjust to proper specifications.
- Improper Valve Seat Alignment, Broken Valve Spring, or Seized Valve: Inspect and repair as necessary.
Engine Fails to Develop Full Power
If your engine isn't delivering the power it should, check for these issues:
- Clogged Air Cleaner: Clean or replace the air filter.
- Poor Compression: Inspect for leaks or wear and repair.
- Incorrect Carburetor Adjustment (Too Rich or Too Lean): Adjust the carburetor.
- Dirty Diesel Fuel: Replace with clean fuel.
- Incorrect Spark Timing: Adjust timing.
- Misfiring Cylinders: Diagnose and repair misfires.
- Overheated Engine: Allow the engine to cool and address the overheating cause.
Engine Overheats
Overheating can cause significant damage to your tractor engine. Common causes include:
- Elongated or Damaged Fan Belt: Replace the fan belt.
- Low Water Level in Radiator: Refill and check for leaks.
- Radiator Shutter Closed: Open the shutter.
- Improper Carburetor Adjustment or Diesel Injection System Issues: Adjust as necessary.
- Incorrect Oil Grade: Use the manufacturer-recommended oil grade.
- Overloading: Reduce load to prevent overheating.
Engine Smokes
White or Blue Exhaust Gas:
This type of smoke indicates:
- Excessive Engine Oil: Check and adjust the oil level.
- Worn or Stuck Piston Rings and Liners: Inspect and replace as needed.
- Incorrect Injection Timing: Adjust timing.
- Deficient Compression: Inspect for leaks or wear.
Black or Dark Gray Exhaust Gas:
This color of smoke is usually due to:
- Overloading: Reduce the load.
- Low-Grade Fuel: Use higher-quality fuel.
- Clogged Fuel Filter: Replace the filter.
- Clogged Air Cleaner: Clean or replace the air filter.
Engine Knocks
Engine knocking is often a sign of:
- Overheating: Allow the engine to cool and address the overheating issue.
- Advanced Spark Timing or Fuel Injection: Retard the timing.
- Lean Carburetor Adjustment: Adjust the carburetor to a richer mixture.
- Excessive Carbon Deposits: Clean the combustion chamber.
- Incorrect Fuel Type or Spark Plug: Use the correct fuel and spark plug.
Excessive Fuel Consumption
High fuel consumption can be caused by:
- Fuel Line Leaks: Inspect and repair any leaks.
- Rich Carburetor Adjustment or Faulty Injector: Adjust the carburetor or replace the injector.
- Poor Engine Condition: Diagnose and address mechanical issues.
- Dirty Air Cleaner: Clean or replace the air filter.
- Adverse Operating Conditions (Prolonged Low Gear, Overloading, Hill Climbing): Adjust operating habits.
Excessive Oil Consumption
If your engine is consuming too much oil, it might be due to:
- Wrong Oil Grade: Use the recommended oil grade.
- High Engine Temperature: Check the cooling system.
- Piston Ring Gaps Facing the Same Direction: Rotate the rings properly.
- Worn or Stuck Oil Ring: Inspect and replace the oil ring.
- Worn Piston Ring Groove, Piston, or Liner: Inspect and replace worn components.
- Worn Crankshaft Bearing or Connecting Rod: Professional inspection and repair may be required.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are key to keeping your tractor running smoothly. If you encounter persistent issues or are unsure about a problem, it's always best to consult with a professional mechanic to avoid further damage.
For more detailed information on tractor engine troubleshooting and repairs, consult your tractor's operator manual or reach out to a certified technician.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can ensure that your tractor remains a reliable workhorse on the farm.



.png)
.png)

0 Comments