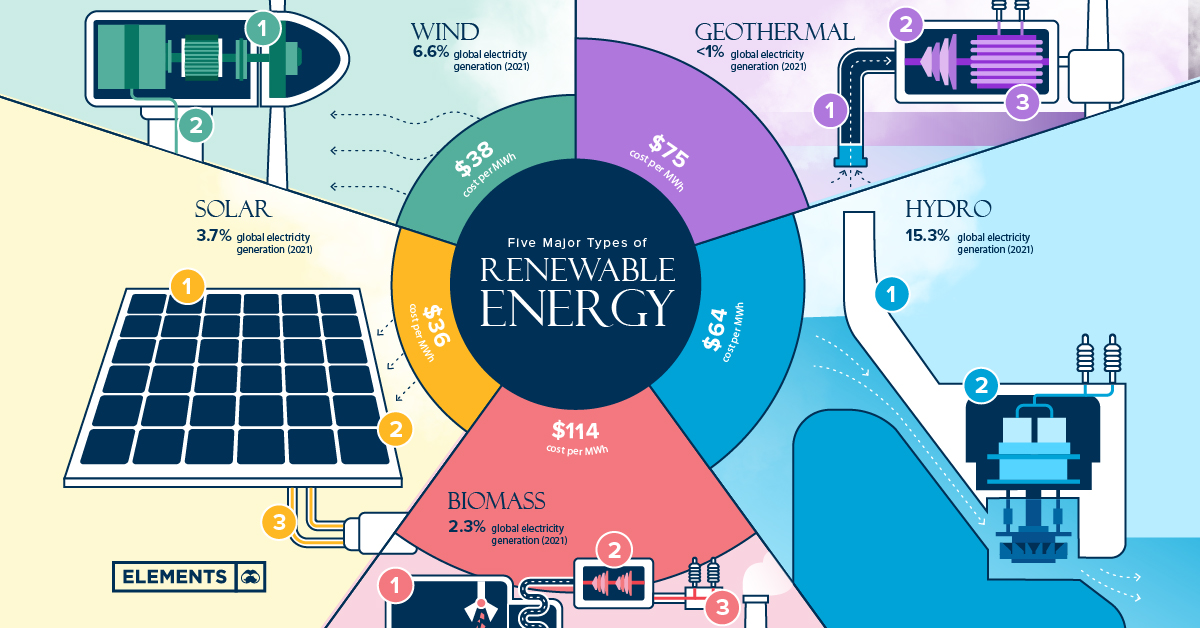
WHAT IS RENEWABLE ENERGY?
Renewable Energy (RE) is energy generated by conversion from resources that do not have an upper limit on the total quantity to be used; are renewable regularly; and whose renewal rate is relatively rapid to consider availability over an indefinite period. These renewable resources include, among others, biomass, solar, wind, geothermal, ocean energy, and hydropower. Renewable Energy is often called “Green Energy” as they come from natural sources and do not emit greenhouse gases (GHG) and other pollutants that are harmful to the environment. Below are the renewable energies which are known as the "BiGSHOW"
Biomass
Biomass resources refer to non-fossilized, biodegradable organic material originating from naturally occurring or cultured plants, animals, and microorganisms, including agricultural products, by-products, and residues. Energy is acquired from these resources when they undergo either thermochemical, biochemical, or physicochemical processes where they produce heat, steam, mechanical power, and electricity.
Geothermal
Geothermal energy comes from mineral resources in the form of (a) all products of the geothermal process, embracing indigenous steam, hot water, and hot brines; (b) steam and other gases, hot water, and hot brines resulting from water, gas, or other fluids artificially introduced into geothermal formations; (c) heat or associated energy found in geothermal formations; (d) any by-products derived from them. Energy is produced in two ways: through natural recharge in which water is replenished by rainfall and the heat is continuously produced inside the earth; and/or through enhanced recharge (hot water used in the geothermal process is re-injected into the ground to pro- duce more steam as well as to pro- vide additional recharge to the convection system).
Solar
Solar energy refers to energy derived from solar radiation that can be converted into useful thermal or electrical energy, which can be used in households, roadway lighting, etc. Solar energy is captured and stored in photovoltaic or solar cells.
Hydro
Hydroelectric power refers to power generated from water resources such as rivers, lakes, waterfalls, irrigation canals, springs, ponds, and other water bodies. Energy is produced by utilizing the kinetic energy of falling or running water to turn a turbine generator. Hydro plants are classified based on their capacities: (a) Microhydro (1 -100 kW); (b) Minihydro (101 kW -10 MW); (c) Large Hydro (more than 10 MW).
Ocean
Ocean energy refers to the energy that can be derived from the wind that is converted into useful electrical or mechanical energy. Initial ocean energy potential sites identified include the Hinatuan Passage, Camarines, Northeastern Samar, Surigao, Batanes Island, Catanduanes, Tacloban, San Bernardino Strait, Babuyan Island, Ilocos Norte, Siargao Island, and Davao Oriental.
Wind
Wind Energy refers to the energy that can be derived from the wind that is converted into useful electrical or mechanical energy. The Philippines, being situated on the fringes of the Asia-Pacific monsoon belt, exhibits a promising potential for wind energy. Wind Energy is usually high on coastlines and mountains. Currently, the Philippines has a wind farm situated in Bangui Bay, Ilocos Norte.



.png)


0 Comments